Is Edge computing the only hope for service providers?
With billions spent on cellular networks, everyone asks about the killer use cases for 5G.
The new 5G Core is capable to provide ultra-low latency services opening the network to potential new user cases, but it can not solve on issue-The distance and latency.
However, this is not the issue of the 5G core either. This relates to physics where latency increases with distance.
That is where edge computing can come to the rescue.
Instead of bringing the traffic to the centralized cloud (in central data centers), which are far, bring the cloud resources to the user itself.
Edge computing brings intelligence to the network edge ( where edge infrastructure is deployed) and thus has shown the potential to open the network for the killer use cases for 5G like autonomous vehicles, connected cars, AR/VR, remote surgery, etc. Also, the increased use of edge devices because of IoT has resulted in a need to take real-time action on the data closer to the network edge.
There are a lot of articles on the internet on “what is Edge computing” but this article is different. As always the case I clarify the concepts by comparison. First, this is your one-stop-shop for understanding edge computing. Secondly, I will clarify the concepts by comparing them with cloud computing, further, also clarify by comparing “edge computing” with Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC).
So stay tuned till the end.
Just one point though, I want to hold the discussion of MEC ( and its difference with edge computing), until I reach the point where I discuss the location of edge cloud as it will clarify the concept to you at that point. However, in one sentence, MEC is a subset of edge computing so the concepts apply equally.
Fair enough? Let’s proceed.
What is Edge Computing and MEC ? (Definition)
We are living in a connected world, With the enormous growth of connected devices, and the demand for ultra-low latency services, the proliferation of mobile devices, edge computing has picked up considerable momentum.
One of the signs of the growing interest is to see how many organizations are involved in the standards. There are many of them in edge computing: ETSI, 3GPP, Linux Foundation, GSMA to name a few, etc.
While each industry body has defined the word “Edge computing” I personally like the one form LF Edge body under Linux Foundation, which is short and comprehensive
“Edge computing represents a new paradigm in which compute and storage are located at the edge of the network, as close as both necessary and feasible to the location where data is generated and consumed, and where actions are taken in the physical world”
For context purposes, I will let me all also add the definition of MEC by ETSI as they own the standardization of MEC, but I will delay the discussion of the “Edge computing vs MEC” to the end as it is important to grasp some initial concepts first.
According to ETSI
“Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) offers application developers and content providers cloud-computing capabilities and an IT service environment at the edge of the network. This environment is characterized by ultra-low latency and high bandwidth as well as real-time access to radio network information that can be leveraged by applications”
So what is Edge computing in in simple terms ?
In simple words, edge computing refers to running “cloud” closer to network Edge. And “close to the Edge” means closer to the user.
But why would one run the cloud closer to the user in a decentralized way?
What are benefits of edge computing?
Reduced latency is the first and foremost benefit. Applications need to run closer to the user to improve the user experience.
But that is not the only benefit.
Reducing backhaul bandwidth is the second most important benefit.
With so many applications running at the edge, many of them, for example, video, sending the data all the way to the centralized cloud is bandwidth-intensive and hence CAPEX intensive too.
Why not just process them at the edge in a decentralized way, thus saving on that bandwidth ? and hence costs.
Hold on! Did someone say “decentralized”?
Isn’t it counter-intuitive to the concept of “cloud”?
Because when we think about the cloud we think of pooling the resources at a central place so everyone can use them.
On the other hand, Edge computing means resources are de-centralized.
So it is the right time to understand how Edge computing is different than cloud computing?
How is “Edge Computing” different than the “Cloud Computing” ?
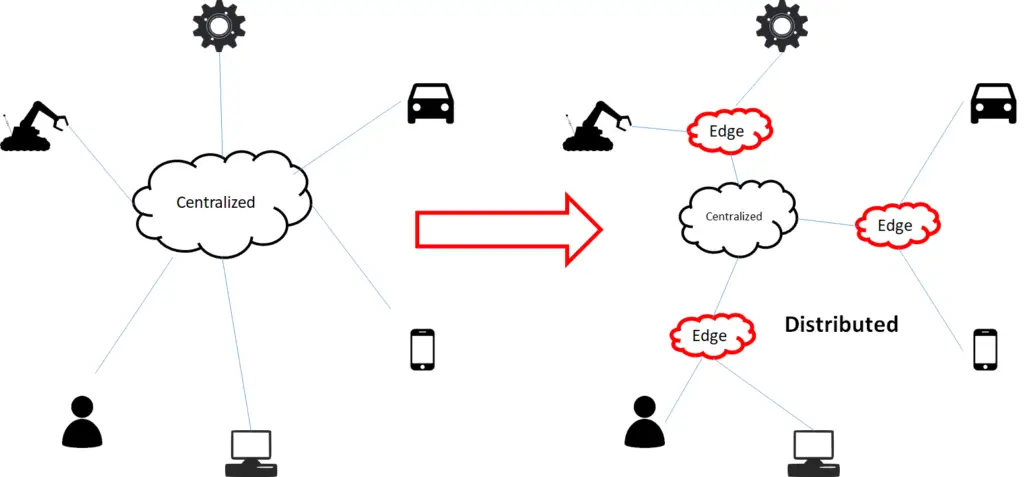
To understand the difference consider the diagram at the left. All the processing and decisions on the data are done at the central place in the cloud computing case while in the edge computing case they are done closer to the user in the Edge cloud ( many clouds distributed).
You must note, HOWEVER, that edge computing is not a replacement for cloud computing. Not all applications run from the edge. Where latency requirements are not high and bandwidth requirements are low, it is always good to run these applications from a centralized cloud to take the advantage of resource pooling.
Also, many applications will need both cloud computing and edge computing. With user-intensive traffic processed locally at the edge and control traffic sent to the centralized cloud.
Therefore although edge cloud would not replace cloud computing, it will certainly reduce the need for it for some applications so it can be scaled down.
Let’s try to compare them on various characteristics.
| Feature | Edge Computing ( distributed ) | Cloud Computing ( Centralized) |
| Compute | Medium to Low computational capacity | High capacity compute resources placed at a central location |
| Latency | Reduced latency as the application is processed in edge | High latency. It depends on how far is the centralized cloud |
| Real-Time data processing | Best for real-time data processing | Does not provide as good results as Edge cloud |
| Backhaul Requirements | Very less as data is served from the edge so no need to see all data to centralized cloud | High backhaul requirements |
| Security Requirements | Higher security requirements as cloud surface is more | High-security requirements |
| Best for what kind of applications | Latency sensitive Or/and Bandwidth intensive | Latency agnostic and the bandwidth needs are low to moderate |
After knowing the difference between Edge computing and cloud computing, it is time to move to understand the characteristics of Edge computing Characteristics/ Attributes of Edge Computing
Edge computing Characteristics
Edge computing/Edge cloud is a cloud, isn’t it?
So it should have the basic attributes of cloud computing, but it should offer more because of the distributed nature of the edge computing
The following are the important key attributes of Edge Computing according to ITU-T Y.3500 and this research paper. I am summarizing them for your easy reference
Now did you notice something?
While the latency and bandwidth are clear benefits that edge computing provides and discussed earlier but additionally edge computing offers network information and location awareness because of the close proximity to the network. This is important as the edge site is near to the access network, an application can take real-time action based on the radio network information ( in the case of the radio access network thus helping real-time applications)
| Traditional Cloud Computing Attributes | Additional attributes because of the Edge nature |
|
|
Where is Edge ? ( Location of Edge Cloud)
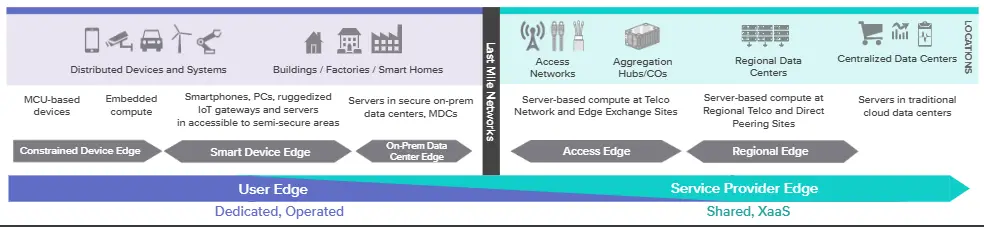
There are two distinct categories of Edge Data Center, the User Edge, and the Service Provider Edge
OK don’t get confused with the names, there are many types of names, there is deep Edge, Far Edge, Regional Edge, enterprise edge, etc..They may all be the marketing terms of vendors
However, as a starting point, I will say focus on two areas here. The service provider Edge and the User Edge. This is taken from LFEdge ( Linux foundation)
Service Provider Edge is where the network of the service providers is present while the User Edge is at the premises of the user. Now it does not mean that the service provider cannot manage the user Edge. In most cases, this will be the case, if a service provider establishes a DC within the premises of the customer OR puts a CPE inside the data center of the customer ( on-prem. edge computing solutions).
But broadly speaking, Service Provider Edge is the edge of the service provider network. A service provider may need to establish a small pop for the edge data center providing similar components as a traditional data center.
On each of these edge locations, you can put edge servers ( edge servers provide compute power)
Did you notice something?
If you look at the Service Provider Edge. The green color is extended inside the User Edge, which means that the boundaries of the service provider edge are not strictly defined. and it can go inside the customer premises also.
Also remember that edge services can be hosted in a private cloud as well as public clouds like Amazon web services, google cloud, and Microsoft Azure.
Service Provider Edge:
The Service provider Edge provides services over the fixed/mobile network infrastructure. This is a shared infrastructure which means it is not dedicated to one end user. CSPs can leverage their fixed and mobile networks at the edge and provide edge platforms closer to the user.
- Access Edge Layer: closest to end device, can be zero or one hop away from the last mile network
- Aggregation Edge Layer: The layer which is one hop away from access edge layer
- Regional Edge: Often closer to Access Edge than the centralized data center.
User Edge
This is on the other side of the last mile network. Normally this is dedicated and customer-owned. Though it can be service provider owned/managed but dedicated for a single customer
- Device Edge : Edge computing capabilities on the device or the user side of the last mile network. Often depends on a gateway in the field to collect and process data from devices. It may have limited compute/storage from user devices( phones, laptops , sensors etc)
- Constrained Device Edge : This category includes micro controller based devices which are highly distributed. They can range from simple functions sensors that have no compute to programmable PLCs that have some compute capabilities
- Smart Device Edge: This includes IOT gateways, smart phones and PCs.
Together the constrained edge devices and Smart Device Edge represent the “things” in IoT
After discussing Edge location, it is the right time to bring in a discussion of Multi-Access Edge Computing ( MEC)
Difference of Edge Computing and MEC
This diagram from LF Edge ( Linux Foundation) clearly shows, “MEC versus Edge computing”.
Edge computing is an umbrella word that includes MEC as a subset. MEC refers to the Telco Edge or the service provider Edge. ( MEC terminology/standards come from ETSI, initially called “Mobile Edge Computing” later on renamed as “Multi-Access Edge computing)
The end-to-end computing that includes User Edge and Service Provider Edge covers the complete scope of Edge computing.
However, MEC covers a subset scope and refers to the Edge computing provided by a service provider.
As shown here, the MEC cloud is offered by the network operator who owns the network. LF Edge also calls it Telco 5G Edge if the operator uses its 5G network to provide MEC services.
However, do note that MEC extends somewhat in the User Edge area also. This would be the use case where a Telco provides CPE at the customer site.

Moreover, network operators/service providers have big potential with MEC/5G. Combined with network slicing, latency-critical services can be provided by service providers with guaranteed SLAs.
And do you know that operators have big leverage in the edge computing industry!
They own the “access network” which gives them leverage over the others. They own the 4G/5G network or broadband network for that matter which neither enterprises have nor the hyperscalers have. This is important as MEC had direct access to the network/radio quality, based on which MEC can take intelligent actions.
Neither Hyperscalers like AWS or AZURE have this kind of access network.
So if hyperscalers would like to deploy their Edge platform locally, they need to work out some sort of collaboration with the operators to use their network/physical sites and have a win-win business model for both.It has a huge monetization potential for Telcos
Use Cases of Edge Cloud
I already mentioned the big monetization potential of Edge computing/MEC. It would make sense to discuss the uses cases at this stage.
As you would see that with edge computing it is possible to bring intelligence to the remote locations. These are only few of the many use cases Edge computing has.
Gaming:
Edge computing enables placing gaming servers closer to the users, thus it is possible to reduce latency and provide a fully responsive gaming experience
Autonomous Vehicles/Self-Driving cars:
Autonomous vehicles require Edge computing servers for extremely low latency, so real-time action can be taken to prevent an accident
CDN and Caching
Video is the most popular service on the internet. Users may face low quality of service because of latency and limited bandwidth to reach remote video servers. Bringing video CDN closer to users can improve the quality of experience of the users. This is not limited to video, but any content can be brought to the network edge.
IoT and Big Data
Edge computing can facilitate computation and storage resources for IoT and Big data closer to the user ensuring a fast response to user requests
Industrial IoT ( IIoT)
With edge computing, industrial operators can perform critical analysis closer to sensors and machines reducing the latency for machine decision making.
Telemedicine
Remote medical diagnosis using telemedicine services will become more commonplace if we have better connectivity between patients and doctors. With edge computing, this becomes easier.
Smart Cities Services
In order to make cities smarter, there should be a lot of sensor nodes installed around the city. These sensors collect various kinds of data from different sources such as weather, air pollution, water level, etc..
Augmented Reality (AR)
AR can provide an immersive media experience to the users. For example in sports stadiums, “virtual cameras” present views from within the field of play, giving spectators the experiences from the perspective of the players themselves.
That’s it about an introductory guide on “what is edge computing and MEC”. With an edge computing model, service providers can monetize their networks effectively and improve customer experiences.
How do you view the potential of the technology, let me know in the comments below.

Hey Faisal!
Just an observation. You may want to correct a typo in the Edge Cloud v.s. Centralized Cloud table, specifically on the Real-time data processing row.
It reads “Does not provide as good results as Edge loud” and i believe it should say “Does not provide as good results as Edge cloud“
Thank you so much Jorge! I will correct it right away