OK, you have heard enough of these terms perhaps from RAN vendors? C-RAN vs Cloud RAN vs vRAN vs O-RAN in the context of Radio Access Network ( RAN)
However, these terms are not clear to you because everyone out there explains them in a way that is enough to confuse many. The fact is that they are confusing as the terms are similar and there is not a lot of difference in them.
That is where this blog can help to explain these technologies related to RAN architecture. It will settle the explanation of these terms, once for all.
And don’t worry, if you don’t know what is RRU, BBU, CU, DU, fronthaul, mid haul; I will explain all these terms as we go through.
Radio Access Network has evolved quite a bit, so it’s important for you to be aware of all these new terms.
Understanding all this will help in understanding a vendor RAN solution.
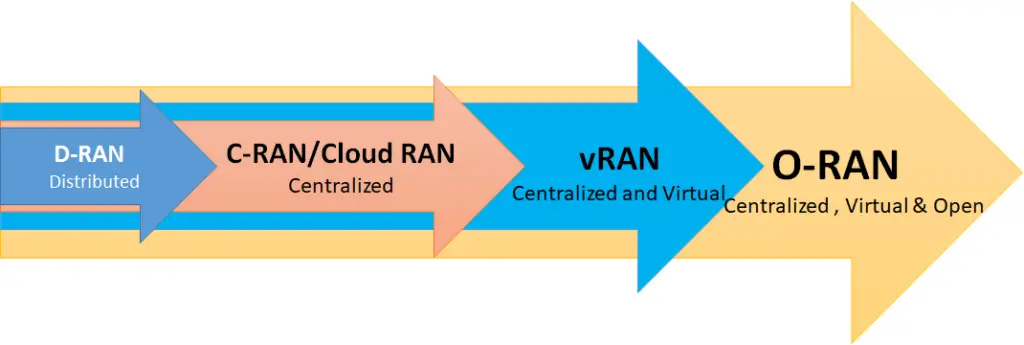
C-RAN vs cloud RAN vs vRAN vs O-RAN vs D-RAN (traditional RAN) ? Is it that difficult to understand?
Not exactly, once you understand D-RAN ( traditional RAN), it is easy to understand the rest of them regarding RAN architecture.
Lets go step by step to understand D-RAN ( traditional RAN) first and then moving to other types
The following diagram summarizes the differences but we will explain it in a moment.
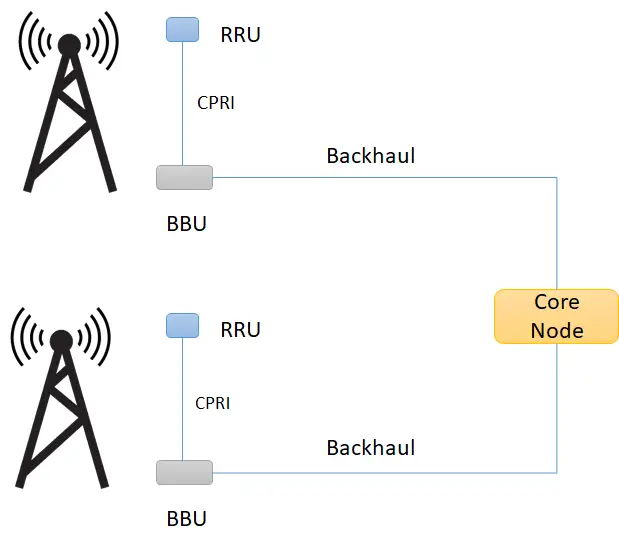
What is D-RAN ( traditional RAN) ?
D-RAN stands for “Distributed RAN”
The diagram below shows distributed RAN. The RRU and BBU are co-located at every cell site. Each cell site with all its radio functions are distributed and connected back to the core network through backhaul.
What is it ?
BBU: Baseband unit. Manages the whole base station, including operating/maintenance and signaling processing. It decides the “CAPACITY” of the system.
RRU: Remote Radio unit interfaces with an antenna on one end and BBU on the other. It connects to BBU through CPRI interface and converts RF signal into data signal and vice versa. Further, it does filtering and amplification of RF signal. In fact, it decides the “COVERAGE” of the system”
Antenna: It interfaces a cell phone wirelessly and transmits/receives RF signal. It decides the “SHAPE” of the coverage.
Reference: ITU-T
What is C-RAN / Cloud RAN
C-RAN (Also CRAN) stands for Centralized RAN or Cloud RAN. In fact, I have seen the industry uses these terms interchangeably.
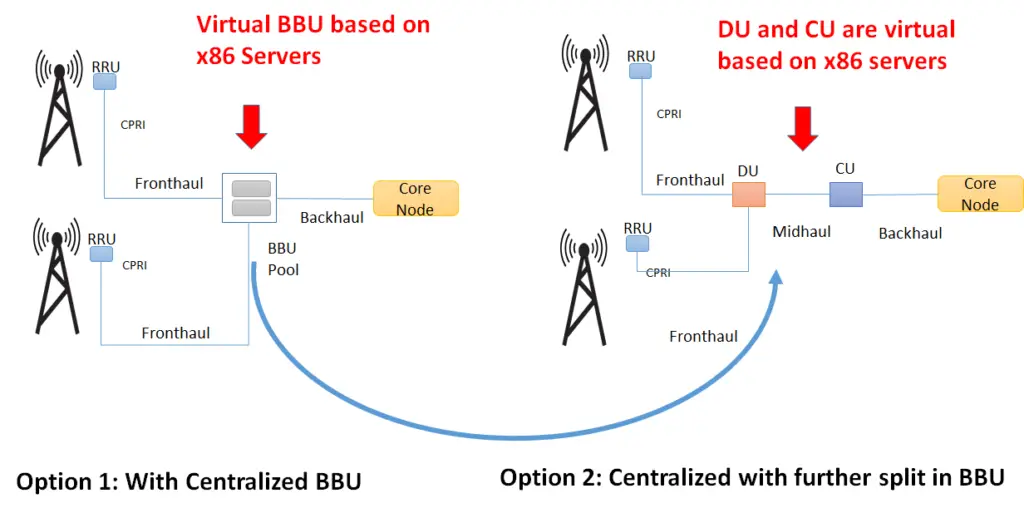
In C-RAN (Cloud RAN) the BBU moves to a centralized location and the cell site only has the antenna and the RRU. This centralization of BBU functionality (also called BBU pool) results in the name centralized RAN or C-RAN.
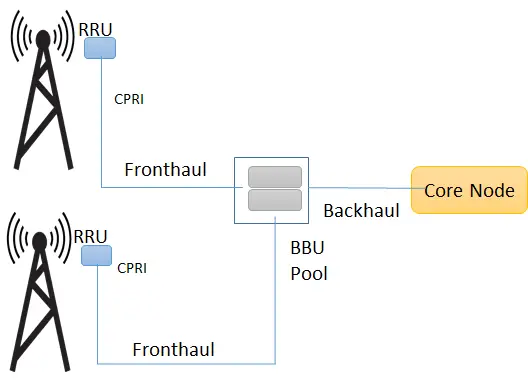
This results in a new interface called fronthaul, which is between the RRU and BBU pool. The benefits of C-RAN includes CAPEX and OPEX reduction as deployment and maintenance cost per cell site are reduced because of BBUs centralization. In addition, it improves spectral efficiency and reduces inter channel interferences, as centralized BBUs can share the resources dynamically among the multiple RRUs. The inter-channel interference is eased because of the joint scheduling and processing.
In addition, a second option of the centralized RAN architecture has a further split in BBUs into DU and CU. Here, CU is further towards the core network resulting in a new interface called midhaul.
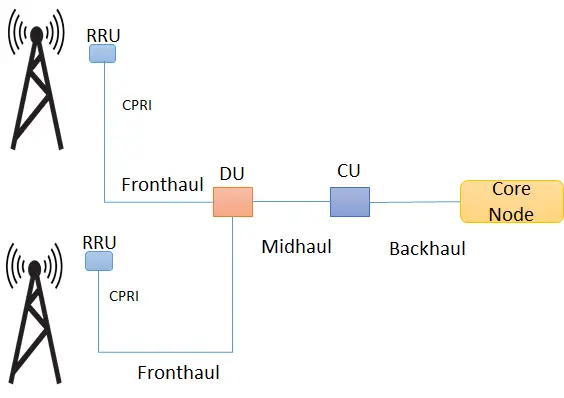
What is it ?
Fronthaul Fronthaul is the link between RRU and BBU (or RRU and DU). It has a strict latency requirements of 100 to 250 µs (one way)
Midhaul: Midhaul is the link between DU and CU.. Midhaul has relaxed latency requirements, which means we can place CU further closer to the core node.
DU: Distributed runs the RLC, MAC, and parts of the PHY layer. We normally place DU closer to RRU.
CU: Centralized Unit handles the RRC and PDCP layers (and SDAP in case of 5G) . One CU can connect to multiple DUs, CU can be co-located with DU or far from DU.
What is vRAN or Virtual RAN?
vRAN decouples the software from Hardware by virtualizing Network Functions. It uses virtualization technologies such as NFV or containers to deploy CU and DU over x86 server. (or virtual BBU on a server). This is like running Functions in software.
So there is no difference between vRAN and C-RAN except that traditionally C-RAN uses proprietary hardware while vRAN uses Network Functions on the server platform. vRAN is infact a type of C-RAN.
Because of vRAN HW/SW decoupling flexibility, we can achieve scalability. This can cause a decrease in hardware costs and application agility as application can be upgraded easily or swapped altogether (which is not easier with traditional hardware).
However, vRAN puts servers to new limits because of the performance expectation. There has been quite an innovation on enhancing server platform to meet the performance needs of vRAN.
 What is O-RAN or Open RAN?
What is O-RAN or Open RAN?
Open RAN/O-RAN (from O-RAN alliance) takes vRAN to the next level. While traditionally vRAN is a closed network, as RU, DU and CU, which are all part of the RAN must be bought from the same vendor.
The O-RAN alliance is working on specifications to open the interface between RRU and DU and further between DU and CU. This means that a customer can mix and match the components from different vendors without being locked to one vendor for all these three components, thus resulting in an open RAN network.
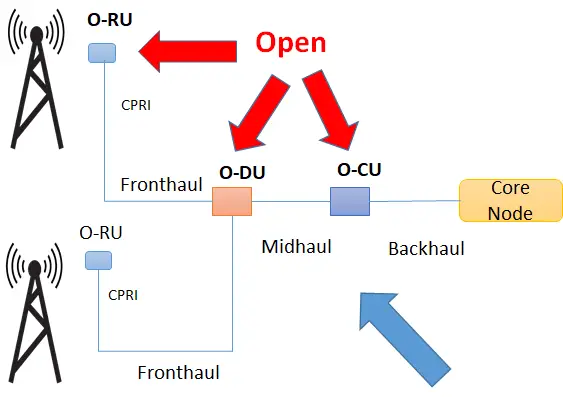
These new open components as per O-RAN alliance’s specs are called O-RU, O-DU and O-CU (where O stands for Open) which is actually a modular base station software stack on off-the-shelf server hardware.
So that’s it about the different between C-RAN , V-RAN and O-RAN. Hopefully, with this you will easily understand a vendor’s solution and also give you an insight on how Radio Access Networks have evolved over the time. Let me know in the comments if the concept is clear to you?

Very well articulated.
Thanks Anand , for taking time to read it.
Very Nice
Thanks Govindraj
Great piece of work Faisal. When it comes to open RAN, both O-RAN Alliance and TIP OpenRAN are involved. Please include ONFs SD-RAN too, so that this becomes a single source of reference for D/C/V/SD RAN.
Hey Anuradha, Correct, However I am writring a dedicated piece on Open RAN which will cover the TIP part also . i will then link it from this article. As Open RAN itself needs a speific article
Described in layman language. Thanks for this really helpful
Thanks Tarun, keep coming back
Great presentation.
Gald that you liked it Anzar
Thank you Faisal. Very helpful.
Great to know that you liked it Nagathega
These acronyms were indeed confusing , specially for an engineer with no background in RAN/BSS.
Very nicely explained..Thanks Faisal sb
On a side note, what are your views on the technology service providers should use for transmission in front haul links, there is an interesting competition between DWDM and POS, would love to read your take on it.
Faisal, as always your new post is a pleasure up to the point with right feeling about what‘s hot by you which is Open–RAN these days. Thank you for your excellent comprehensive summary about the synonyms around O-RAN topic. I‘ve forwarded your article to my esteemed colleagues for internal joy and leisure and external distribution to partners and customers as recommended reference. Looking forward to your next post, have a good weekend, best regards from Cologne/Germany – Thomas
Hey Thomas, you made my day with this comment….Happy visiting…
very well explained
Thank you so much Rahul
thank you for making these concepts easier to understand, especially for someone who has minimum background in wireless networks
Thanks Marjory Sy for commenting and coming back to read them blog
complexity Simplified. Thanks Faisal
Thank you so mmuch Ansar Bhai ! for taking time out to read this piece.
Excellent explanation as always!
Excellent explanation. Thanks to your detailed description. It is really helpful.
Hey Kidane, Thanks a lot, please do me favor and share it to your circle, so it can help somone
Very well described in short..
Thanks Anurag
Thanks, Faisal for well-articulated nuggets of aspects of RAN.
it was very useful for aspirant.
Thanks a lot Batakrushna Malik
Great article! So why would telco provider go o-ran? From my experience seems like they might do that for competition on price. But this might be traded off with more comples interconnectivity between diggerent vendors.
Well articulated for a green hand into the 5G/Telcom industry, it is really helpful, thank you!
Thanks Lin YenYu, glad that you liked it
Thank you for this useful article. Well communicated.
Thank you Thamas !
Well briefed
Thank you Muhammad Fahad
Really well-explained post on RAN transition…
Thank you~~~
Thank you Simyung !
Good Article!
Thank you so much Jigish, Sorry for replying late as I had mail issues
Well explained
Thanks Jagpreet. Sorry for replying late as I had mail issues
Perfectly and precisely explained. Good Job Done! Thank You Faisal!
Thanks Abshek Singh, for dropping by and commenting
Perfect Explanation
Thanks for the feedback Subbu
Well Explained.. Thanks for sharing
Hi Jintendra, thanks for visiting and commenting
beautifully comprehended content with diagrams
Thank you Sharada
Helpful summary. Thank you!
Thanks Robert !
I really like it.
Thanks Murat
Excellent article sir. As a student pursuing MBA in Telecom tech, it was really very insightful
Thank you Babuji
Very good and All the different RANs Explained very well
Hey Kumaran, thank you for visiting the blog
Great article
Thank your Hesham for commenting.
Thank you, this was a great write up
Very well articulated in a simple way. Thanks a lot
Thanks a lot Ritesh, please keep coming back
Hello:
The article looks interesting.
But in terms of the CRAN and Cloud RAN, I see them, like different now.
-When we talk about C-RAN that is centralized RAN, where you have all the BBU processing capacity in a central site, and the RRU and Antenna in each site.
-Cloud RAN, implies the possibility to include part of the NodeB capacity in the Cloud, and you have in the local site: RRU, antenna, and maybe some part of the Node.
-So Cloud RAN, would be in the last part of the evolution, close to the O-RAN.
Best regards,
Carlo
Thanks a lot Carlo for taking time to read and interpreting it correctly.
Hello, great article!
One question, so for vRAN, do NEPs also provdie proprietary HW+SW or they also use COTS + CaaS from e.g., HP + WindRiver? If they use COTS + CaaS, it’s not a closed system right?
Hi Network Geek. Thanks, vRAN is a closed system from interface point of view but open system in a sense that it is disaggregated in terms of HW and SW. The only truly open system in O RAN
Hi Faisal,
What is the future of O-RAN? Will it really happen considering that vendors would like to influence their own products in the total network. Presently products with RRU + BBU integrated are coming out. What is the future of those products?
Very well explained .
Hi
Thank you so much for your amazing information on different RANs.
How each one of RANs can help to reduce energy consumption in mobile networks?
Thanks