The “Overlay vs underlay” discussion is important as overlays are everywhere in networks- in the Datacenters (DCs) and in SD-WAN.
And there are many tutorials out there explaining overlays and in particular difference between overlay and underlay. However, they are difficult to understand, and more importantly, they do not address the most important point – what problems overlays are trying to solve. What are the limitations in the underlays that triggered a need for the overlays?
Therefore this blog takes you step by step on the concept of underlay, its limitations, and how overlay solves it.
I will do so using SD-WAN as a reference, but the concepts are the same in the Datacenter i.e SDN in Datacenter also uses the concept of overlays.
Difference of Overlay and Underlay networks in summary
Overlay vs underlay in summary
An Underlay network is the physical network responsible for the delivery of packets like DWDM, L2, L3, MPLS, or internet, etc. while an overlay is a logical network that uses network virtualization to built connectivity on top of physical infrastructure using tunneling encapsulations such as VXLAN, GRE, IPSec.
Why overlay networks are important and worth discussing?
Do you know that traditional routers and switches are hardware-centric and perform packet forwarding based on the destination IP address, therefore network segmentation and multi-tenancy are not possible.
This creates the following inefficiencies and drawbacks: Network segmentation and network slicing are not possible – duplicate IP address ranges cannot traverse a single IP network natively; Scaling is hard. VPNs can solve these issues albeit with some inefficiencies as they are very transport medium centric and explained below.
On the other hand, the overlays bring the flexibility that underlay is not able to provide. Overlays have been there for a quite while but with the SD-WAN they have become very popular.
This blog uses the example of SD-WAN, but the concepts and advantages are exactly the same for the Datacenters, you will just replace the CE router with a virtual machine ( VM) that needs to communicate with Spine switch which is the CE a the HQ in this example. The underlay network is the MPLS here, it can be any routing protocol in Datacenter like OSPF, BGP, etc.
Let’s start to understand underlay before going to overlay
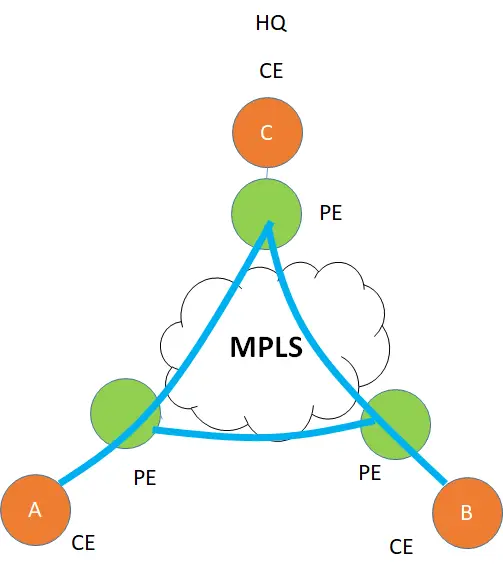
Let’s take the example of a common physical infrastructure for example a WAN network, In which a customer has three sites A, B, C with the C as the HQ which are all physical devices. There is a layer 3 IP/MPLS VPN between the 3 sites which is the underlay for this customer.
This is a Peer-based VPN, which means that the CE ( Customer Edge) peers with PE ( Provider Edge router), exchange routes, and then how the routes are advertised between the PE is the responsibility of the MPLS provider and not the customer who owns CE. Once CE handovers traffic to PE, it forgets on how it is transported inside the Provider network and which route it takes.
What problems underlays cannot solve?
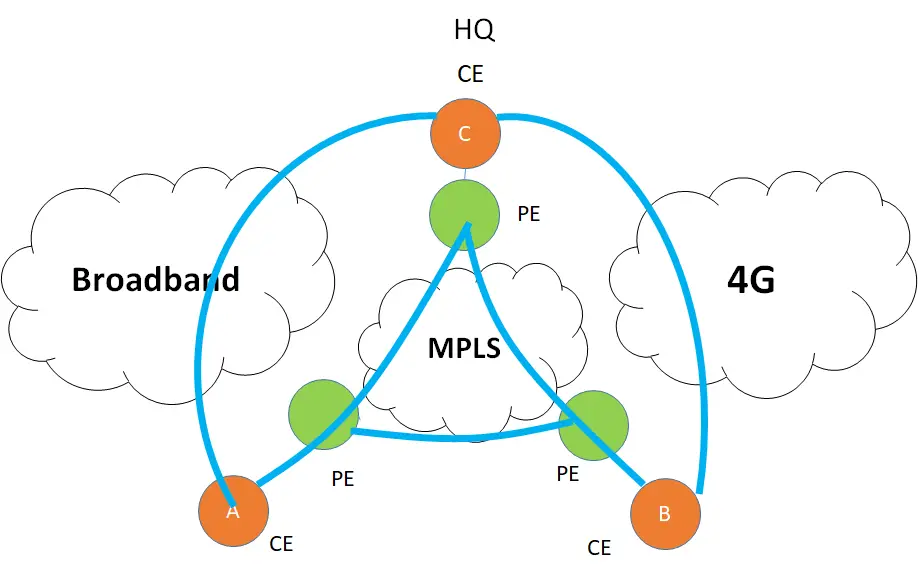
While the above shows a simple example of a Layer 3 underlay. Things have changed beyond the use of just “MPLS” for transport. Think of it! internet is everywhere. High-speed data is cheaper than before. Exploiting the use of the internet for carrier transport is just a natural evolution then.
To understand the concept of overlay, I introduced two more networks. A broadband network and the 4G network. The need is to use these “low cost” transport networks to offload some of the data from the MPLS network ( if not all)
There are some issues here :
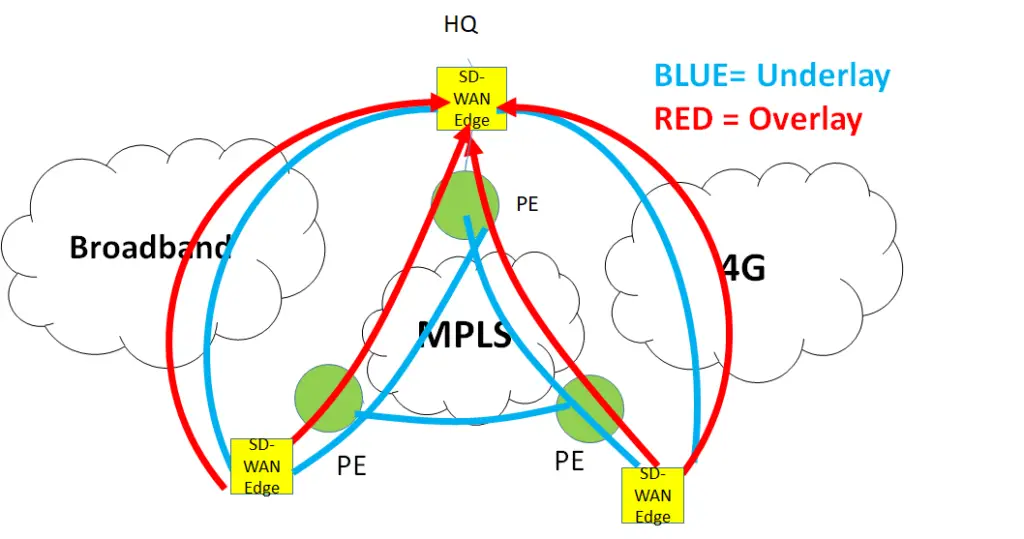
Issue 1: The Internet cannot be used as an underlay for private traffic
The first issue is that internet medium natively is insecure so it cannot be used as an underlay for private traffic. To protect it we will need to use security protocols like IPsec. IPsec is a tunneling protocol. Which is an overlay. ( but we wanted to solve the issue with underlay, isn’t it? )
Issue 2: Transport Dependence is too restrictive
Let’s for the moment assume that the internet is secure so we kill the first argument against the underlay. The customer wants to divide the applications between the different circuits ( for example YouTube on 4G, A SaaS app on broadband, and email on MPLS). Further, he wants to use the backup of MPLS as broadband. All this is possible but very complex and static which means if the customer wants to change the application’s distribution over the circuits. He needs to change his configurations which is operationally NOT easy. To put it simply the configurations are hardware-specific, which means they are specific to the physical underlay and complex to change.
Issue 3: Multi-Path forwarding
The customer wants load balancing by combining underlays of different types.
However, it is very complex ( if not impossible) to use multiple underlays which are of different types, simultaneously to forward traffic from source to destination.
Welcome to the Overlay Networks. The software instead of hardware is the solution
Until now we learned that if we stick with the underlay, it can restrict us in multiple ways. In order to get transport independence, overlays can come to our rescue.
Overlays are software-based and not dependent on transport. It’s like a virtual network ( virtual links) on top of the physical network. This virtual network needs to have underlay created first.
The trick is simple. Create an underlay once and forget it. Now create overlays on top of it and since they are software-based. changing the configurations is super easy and friendly. Underlay is a pipe on which overlays run. The intelligence is all in the overlay.
However, to have overlays in SD-WAN, we will need a special CPE called SD-WAN edge device. These overlay nodes are installed at all the sites.
How Overlays are formed?
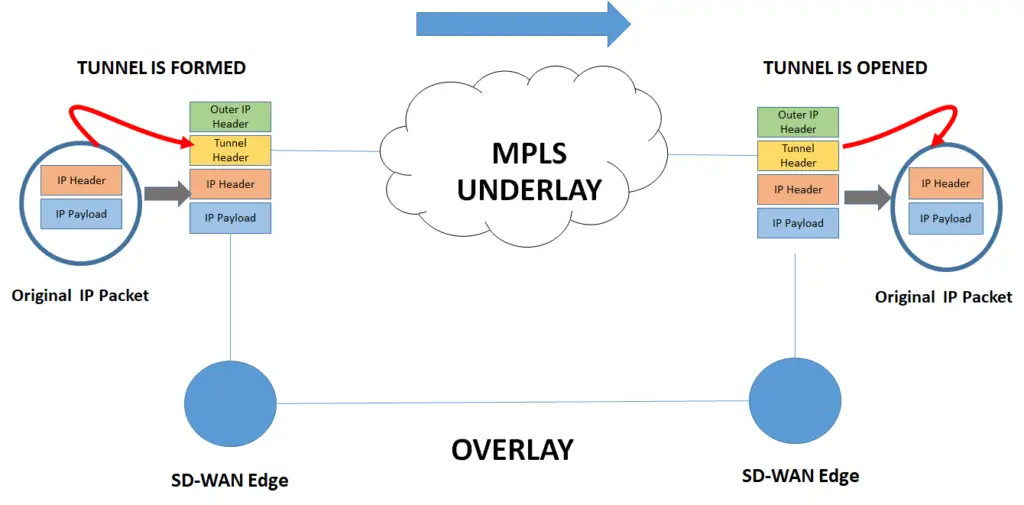
The following example shows a GRE tunnel formed by SD-WAN Edge Device. The edge device adds a GRE tunnel header with a new IP header and masks the inner IP header from the MPLS domain, the MPLS forwards based on the outer IP header.
Once the packet reaches its destination, the SD-WAN edge removes the outer IP header and the Tunnel header and what we get is the original IP packet. During all this process the overlay is not aware of the underlay.
The same process can be done for the internet underlay but with the addition of encryption using IPSec. All this can be done seamlessly using the same SD-WAN Edge box.
The overlay is formed once encapsulation happens at the left SD-WAN box and ends when the header is removed at the destination. The overlay is not aware of the underlay on which it is riding. The underlay here is MPLS but it can be any other type of transport.
How Overlay networks solve the issues ( Advantages of Overlays)
1, the Security issue is solved by using encryption. A Public underlay such as the internet is not trusted. SD-WAN edge solved that issue through the use of IPsec ( This solves issue 1 above)
2. Transport Independence. The same SD-WAN overlay can seamlessly connect to multiple different media like the internet, MPLS, L2 media, etc. The overlay does not care about transport media as it is using tunnels. With this, it opens the world of innovation and flexibility in the services. The intelligence is now in the software and not in the hardware. The applications can be dynamically forwarded and distributed between the 4G, broadband, and MPLS. There can be multiple ways in which traffic can be protected between different transport media. ( This solves issue 2 above)
3. Considering overlays are transport agnostic, there is no limit on the number of multi-paths that can be used in overlays to carry traffic from source to destination for the purpose of load balancing. This makes overlays very scalable.
So in summary overlays wins in all cases and that’s why they have become popular these days.
Overlay vs Underlay in summary
| Items | UNDERLAYS | OVERLAYS |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Underlays networks are the physical networks responsible for the delivery of packets like DWDM, L2, L3, MPLS, or internet, etc. | while overlays are a logical network that uses network virtualization to built connectivity on top of the physical network using tunneling encapsulations such as VXLAN, GRE, IPSec. |
| Encapsulation | Does not require encapsulation | Requires encapsulation such as VXLAN, GRE, etc |
| Application Segregation | Very complex to divide applications across different underlays | Very easy to achieve this |
| Hardware or software | Hardware-based connectivity. | Software-based connectivity |
| Multi-path forwarding | Complex to set up multipath forwarding | Inherent support for multipath forwarding |
| Scalability | Limited scalability as hardware-dependent | More scalable as software-based and because of the multi-path capability |
| Security | Physical underlay such as the internet is not secure | Security can be easily added using encryption methods such as IPSec. |
| Deployment time | Long deployment cycle as hardware-dependent | Quicker deployment time. Adding and changing services is very quick |

Thanks for the write up. It helped to further clarify demarcation between overlay and underlay. SD-WAN has brought the concept to mainstream application. What do you think of MEC 3.0 SD-WAN Standards? Is it relevant or too late with SASE sweeping over? https://www.mef.net/service-standards/overlay-services/sd-wan/
Thanks in advance.
Hi Anand, thanks, MEF SD-WAN standards by MEF are good and in thr eight direction. They are not late….In fact they are actively working in SASE area….sorry for responding late, it seems I have issues with comment notifications not reaching me
you are an amazing guide in networking and virtualization
Hi, love this comment Nidhi. thank you for coming and commenting !
Hi Faisal,
One of the best blog where i can understand how network’s are evolving now a days.
Given the SD-WAN landscape, do you see a miniature version of SD-WAN coming to market which can help the enterprise customer than service provider.
Thanks,
Iyappan
Hey Iyappan, thank you, it is possible today. SD-WAN runs in two models. Either SP can provide it or the enterprise can buy it directly from SD-WAN vendor and run it…. Both these models are very much present today
very well explained. only article where i can understand overlay and underlay.
That is good to know Hemant !
Thank you for this information. For my level of understanding it is just what I needed.
Very much appreciated.
Thats good to know ! Kenton
Great explanation.
Thanks Hans ! keep coming back
Great breakdown of overlay and underlay in SD-WAN! I appreciate the clear explanations and examples provided. This easy guide makes it much simpler to understand how they interact in data centers. Keep up the great work!
Great explanation of Overlay and Underlay in SD-WAN! I found the comparison really helpful for understanding how they work together in data centers. The easy guide format made complex concepts much clearer. Thanks for sharing!