For a while I thought to write about an OpenStack cheat sheet showing OpenStack components, so you can refer to it as an easy to use handy reference.
If you are using NFV, you are using OpenStack for sure. OpenStack sits at the VIM layer inside NFV MANO and is the most important piece to manage the cloud infrastructure. For a quick refresher on NFV, click here, NFV Cheat Sheet.
Openstack is very complex. You hear a lot of terms like Cinder, Glance, Nova, Horizon, etc. They are quite confusing to know and remember. So here I made a small OpenStack cheat sheet as a diagram/infographic which you can keep as a reference. Just match the block colors with the colors of lines and you will easily know the role of each component/block and how they interact with the other blocks.
How about sticking a copy of the diagram on your desktop for easy reference !
What is OpenStack?
“OpenStack is a cloud operating system that controls large pools of compute, storage, and networking resources throughout a datacenter, all managed and provisioned through APIs with common authentication mechanisms”. “https://www.openstack.org/software/“
So here is the cheat sheet/infographic about Openstack services.
Do take a note however that there are many more services in openStack, here are the most important core ones that you must know
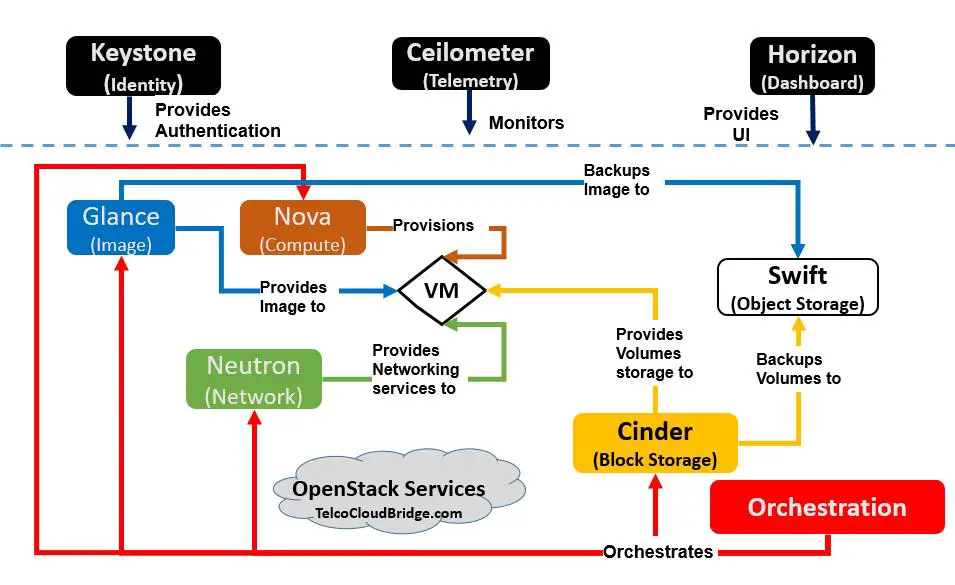
Description of OpenStack Cheat sheet
Horizon ( Dashboard)
This allows users to work on OpenStack using web GUI instead of CLI. This provides a user-friendly dashboard. This is part of common services
Ceilometer ( Telemetry)
The ceilometer is a component of the Telemetry project. Its data can be used to provide customer billing, resource tracking, and alarming capabilities across all OpenStack core components.
Keystone ( Identity)
keystone is the simplest service in OpenStack. it is a core service and provides authentication and authorization of tenants in OpenStack.
Nova ( Compute)
Nova is the original core component of openstack and considered one of the most complicated components in openstack. It providess compute service in openstack.
It has various components:
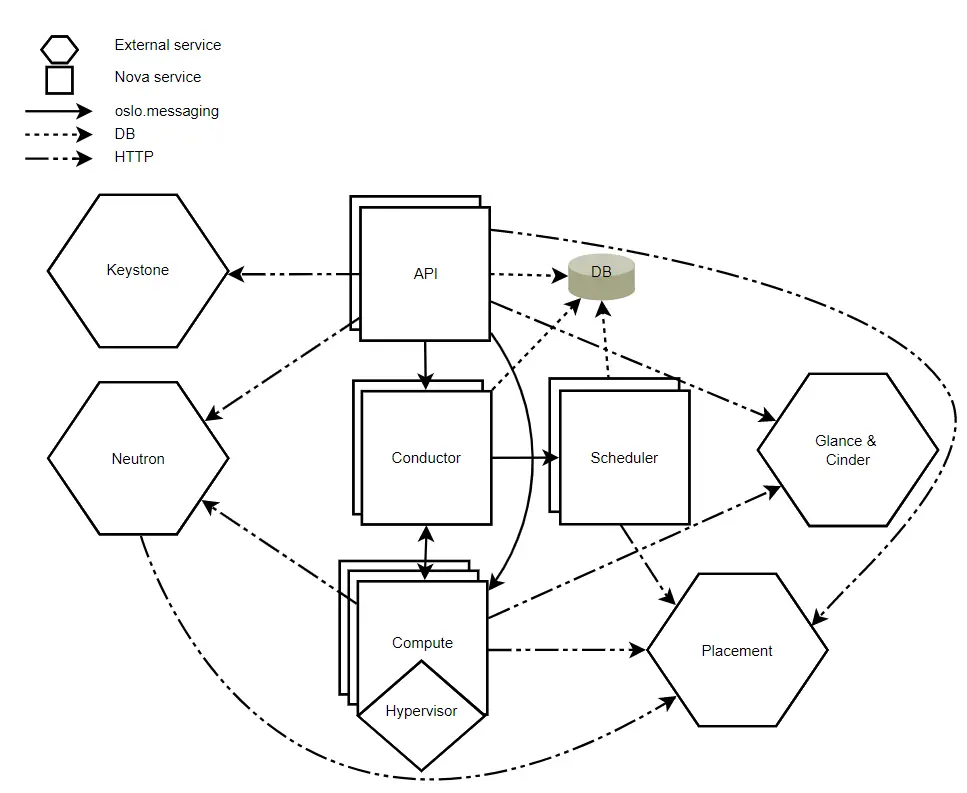
Nova-Compute
The nova-compute is responsible for creating and termination of VM instances via hypervisor APIs ( for example Libvirt KVM, VMWare API for VMware)
Nova Conductor
The Nova conductor provides database access to compute nodes. The logic is to have all the database access pass through Nova conductor instead of compute nodes accessing DB directly thus reducing the risks in case of compute node gets compromised.
Nova-api
The nova-api component accepts and responds to the end user and computes API calls.
Nova-Scheduler
Compute uses the nova-scheduler service to determine how to dispatch compute requests. For example, the nova-scheduler service determines on which host a VM should launch.
Neutron ( Networking)
Neutron is a service that provides networking service to other components of OpenStack
Storage
There are various type of storages in openstack. It is important to understand the difference between them
Cinder (Block Storage)
Cinder provides block storage in OpenStack. It provides raw volumes that can be used as a hard disk in virtual machines. It is called block storage because a large amount of data is chopped into blocks and stored with a unique identifier is attached which allows the data to be retrieved quickly and efficiently.
Use Cases:
- Databases-Block storage is common in databased and other mission-critical applications that demand high performance
- Volume snapshot management
- Attaching or detaching volumes from instances etc
- Creating and deleting of a snapshot of the volume.
Swift (Object Storage)
Swift provides an object-based storage service and accessible through Rest APIs. It can easily scale, making it a great choice for public cloud storage.
It has static nature and writing objects is a slow process, so does not work well with traditional databases. ( for which cinder works well). S3 from Amazon is a good example of object base storage.
Glance (Image Registry)
Glance also provides storage but acts only as an image registry. It keeps track of virtual machines images, metadata such as the kernel, disk images, disk format, etc. This is available to OpenStack users through REST APIs.
Heat- Orchestration
Heat manages and automate/orchestrates entire life cycle of infrastructure that includes servers, IPs, volumes, security groups, users etc.
So thats it about the core services in OpenStack; let me know in the comments if you have any comments on this piece and if this cheat sheet helped you or not.

Great stuff Fisal. If anyone wants to understand NFV MANO stack and VIM, you may check https://youtu.be/mM17YzOslRw